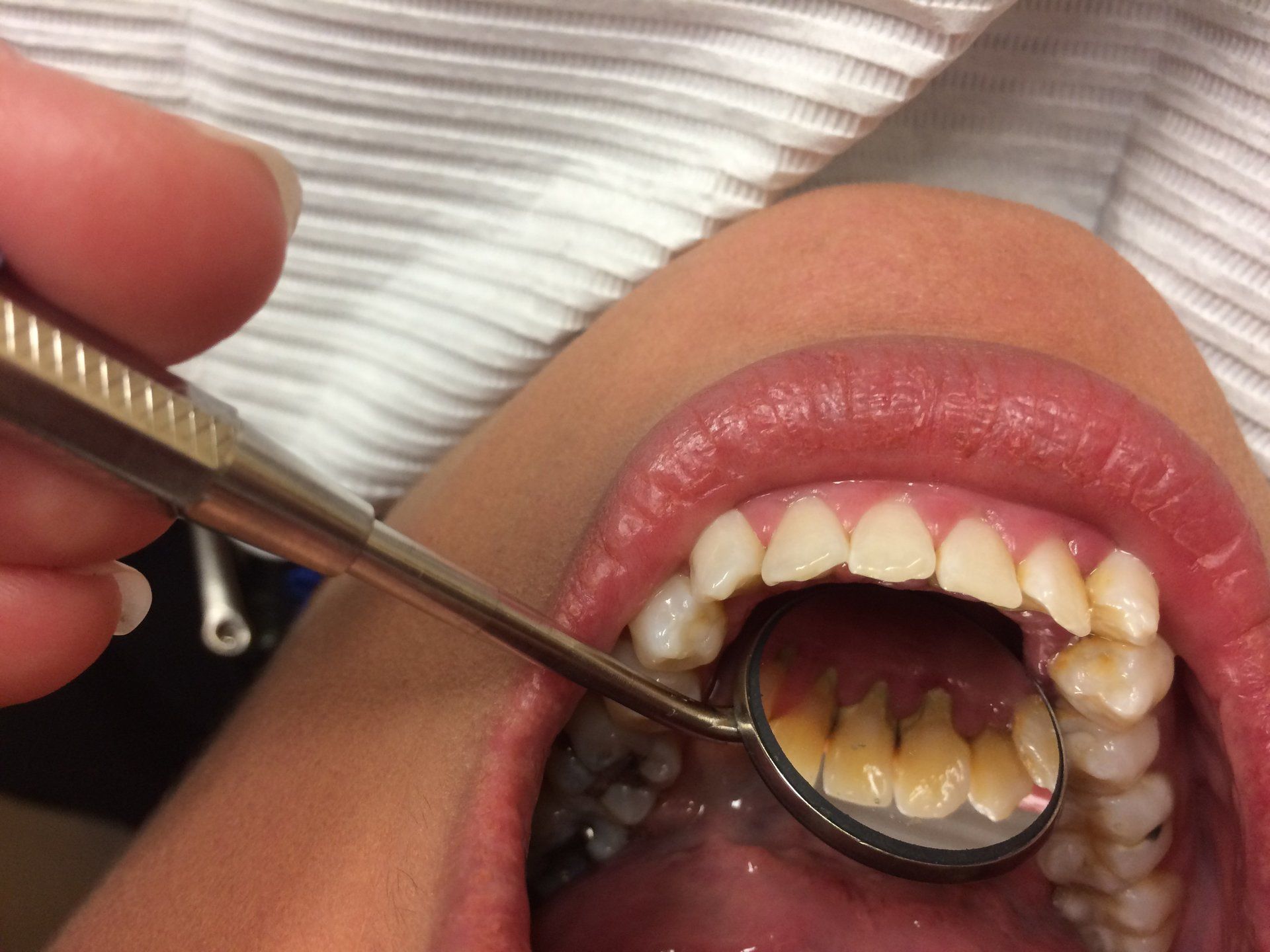
Swollen Gums:
Perio/Endo abscess. If it is gum related, you have likely lost bone from disease or a fracture, and now have a deep gum pocket which is accumulating bacteria. You may have a bad taste or odor. Rinse with hydrogen peroxide, use dental tooth picks and proxy brushes to clean thoroughly. See your dentist for root planning, and Peridex® rinse. You may need to take Periostat® medication or treat locally with antibiotics. You may need a root canal if the nerve is also involved. A Periodontist, gum specialist, can help save your teeth if your dentist can't. Get a second opinion before having your teeth pulled. Sometimes the tissue behind the last or erupting 3rd molar swells and hurts. A condition known as Pericoronitis. Antibiotics, cleaning as stated before, and trimming the gum will help. Extraction of the wisdom tooth is usually necessary.
Pus Bubble on Gum Tissue
Pink or reddish draining point of infection from tooth or gum abscess. You need a root canal. Will slowly go away after infection is treated. May leave a scar. Infection will not completely go away without treatment. Most often tooth abscesses will not infect the sinus due to the protective membrane lining the sinus. Additionally, bacteria can pass from one person to another, but infections are not considered contagious. A person's tooth infection will not infect the tooth of another person without another cause. You should not attempt to drain the head of the bubble using a pin, as you may push the infection deeper into your facial spaces. Take antibiotics.
Upper Jaw Pain or Pressure
Commonly from a sinus infection or dental abscess. Occasionally from a blocked duct or inflamed parotid gland when sweets or bitter flavor cause a stinging pain.
a.) Sinus problems:
If your tooth feels long, aches, itches in the gum, vibrates when you walk, worsens when upside down, and putting pressure on your face next to your nose hurts, you very likely have a sinus infection. Pressure will be felt, but it won't appear swollen. In some cases, teeth may also become sensitive to cold due to increased bruxism; Your body's way to relieve sinus pressure. Breathing steam, using a decongestant and nasal spray to open passage ways to the sinus for drainage, and taking Airborneª to improve your immune system, will help. See your dentist or physician for treatment and antibiotics if it lingers, especially if pain developed after recent surgery.
b.) Dental abscess:
constant ache, unlike with a sinus infection where a few teeth hurt, one tooth will start to ache keeping you awake at night. Check if you see a large hole on the tooth, or if any teeth are loose or sensitive to heat. You may need root canal therapy.
c.) Shingles, mumps, or neuralgic pain disorders- seek medical advice.
Lower Jaw Pain
From muscles or teeth.
a.)
Bruxing and dental treatment can cause myofascial pain, or cheek pain. It may feel like a big knot when the muscle spasms in your cheek. It hurts to chew, but warmth makes it feel better. If none of your teeth severely hurt, nor does pushing along the gum area, take Advil, use a temporary store bought night guard, and put warm, wet compresses on face. You can get a mild muscle relaxant from your health care provider, like Valium, if needed. Massage and stretch the area. Soft diet, no gum chewing, or clenching. If symptoms recur, see dentist for permanent occlusal guard, bite equilibration or rehabilitation, or orthodontic treatment.
b.) Abscess- If a lot of pain is coming from a tooth such as tenderness or swelling in the gum underneath and it is discolored or slightly loose, you most likely have an abscess. The swelling will increase with applied heat. Use ice only if it lessens the pain. -see your dentist.
c.) Pericornitis- A gum infection from erupting lower 3rd molar. For immediate relief, you may have the upper opposing 3rd molar removed if it is biting on the lower tissue, and the lower 3rd molar scaled and irrigated with hydrogen peroxide. Take antibiotics such as pen vk 500mg or clindamycin 300mg four times a day if severely infected. The lower molar should be removed when symptoms resolve.
d.) Shingles, tumors, or neuralgic pain disorders-
seek medical advice from an ENT doctor
Loose Tooth
Lack of bone:
See a periodontist for root planing, bone replacement surgery, and possibly a root canal.
Recent trauma:
An injury may heal itself. If it has slightly moved, you can gentle move the tooth to its previous position. For larger movements see a dentist asap. If the tooth has come out, put it back in the socket. If it is dirty, rinse with saline, or milk and put back in the socket. Don't tooth the root. See a dentist asap prefer within 1/2 hour. If the tooth has been fractured, only put a temporary filling without drilling or additional trauma. In all cases, except sometimes complete fracture, root canal treatment is likely needed.
Abscess:
Root canal treatment or gum therapy with antibiotics will tighten up the tooth when the infection clears.
Tongue Problems
a.) Pain-from yeast, trauma, or other medical conditions- seek medical advice if doesn't go away in a few days.
b.) Coating or discoloration (white or black)- can be from plaque, yeast, or over grown tongue fibers (AKA Hairy Tongue) of which can temporarily stain over time, or when using rinses such as Peridex®. Brush the tongue with a mix of hydrogen peroxide baking soda and scrape the tongue daily with a hygiene device to remove plaque. For yeast use topical anti-fungal. Consult dentist. White lines are typically from a non-pathologic disorder "Geographic Tongue."
c.) Sores-
some are canker sores which can reoccur, but are not contagious, possibly the result of an allergy, stress, acid reflux (read our dental news page), or vitamin deficiencies. Trauma from injury or rubbing tongue against a rough tooth will cause an ulcer. Rinse with salt water, use finger nail file to take off sharp edge of broken tooth if you can't see a dentist, put wax or gum on the inside of teeth to keep tongue away for a day or two. Have teeth reshaped or adjusted, possible needing orthodontics to correct bite.
d.) Cancer- usually painless, a unilateral sore or thick patch of skin that persists. Tongue carcinoma is usually located on one side or under the tongue. It may look white, red, or a mixture. High risk people are generally over 40, smokers, consume alcohol or drugs, poor oral hygiene, poor nutrition or health, and sometimes with family history. For people that are not in this group, look for other causes first, like a sharp tooth or filling, liquid or pizza burn, or benign disorders such as Geographic Tongue or Lichen Planus, before getting a biopsy. Many dentist can screen for cancer, or you may seek medical attention through an Oral Surgeon or ENT.